leeb hardness test method|types of rockwell hardness test : factories The Leeb hardness testing method uses a conical indenter and ball indenter to measure the hardness of a material. This article explains how this method works and its applications.
Resources related to disinfection and sterilization for healthcare settings.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Lames de terrasse pin autoclave traité classe 4 (CL4) vert striée. Dimensions 27 mm x 145 mm x 5,00 m. Lames de terrasse bois résineux avec un excellent rapport qualité/prix. Lames de pin .
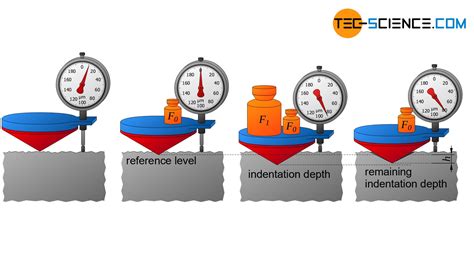
units for rockwell hardness test
The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material .The traditional methods are based on well-defined physical indentation hardness tests. Very hard indenters of defined geometries and sizes are continuously pressed into the material under a particular force. Deformation parameters, such as the indentation depth in the Rockwell method, are recorded to give measures of hardness. According to the dynamic Leeb principle, the hardness value is derived from the energy loss of . The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material tested.
The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces (mainly above 1 kg).
The Leeb hardness testing, otherwise called as Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT), is considered as one of the four commonly used methods to test the hardness of the metal. It is a type of non-destructive testing used to inspect large sized workpieces weighing above 1 kg.
The Leeb hardness testing method uses a conical indenter and ball indenter to measure the hardness of a material. This article explains how this method works and its applications.1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Leeb hardness of steel, cast steel, and cast iron (Part A), including the methods for the verification of Leeb hardness testing instruments (Part B), and the calibration of standardized test blocks (Part C). 1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to impact velocity of a moving impactor is used to determine the hardness.
ISO 16859-1:2015 covers the determination of a dynamic hardness of metallic materials using seven different Leeb scales (HLD, HLS, HLE, HLDL, HLD+15, HLC, HLG).
Metallic materials — Leeb hardness test — Part 1: Test method 1 Scope This part of ISO 16859 covers the determination of a dynamic hardness of metallic materials using seven different Leeb scales (HLD, HLS, HLE, HLDL, HLD+15, HLC, HLG). 2 Normative referencesISO 16859 consists of the following parts, under the general title Metallic materials — Leeb hardness test: — Part 1: Test method. — Part 2: Verification and calibration of the testing devices. — Part 3: Calibration of reference test blocks.
Governed by the ASTM A956/A956M standard, this method utilizes the Leeb hardness principle to deliver fast and accurate measurements essential in various applications, from quality control to on-site metal hardness evaluation. The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The results obtained are indicative of the strength and dependent on the heat treatment of the material tested.The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces (mainly above 1 kg).The Leeb hardness testing, otherwise called as Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT), is considered as one of the four commonly used methods to test the hardness of the metal. It is a type of non-destructive testing used to inspect large sized workpieces weighing above 1 kg.
The Leeb hardness testing method uses a conical indenter and ball indenter to measure the hardness of a material. This article explains how this method works and its applications.1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Leeb hardness of steel, cast steel, and cast iron (Part A), including the methods for the verification of Leeb hardness testing instruments (Part B), and the calibration of standardized test blocks (Part C). 1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
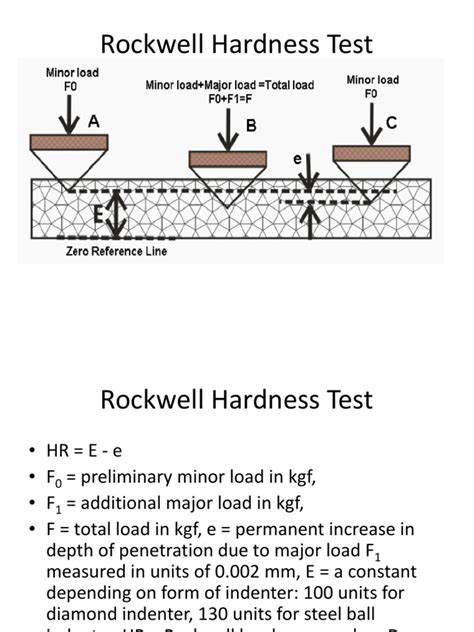
types of rockwell hardness test
Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to impact velocity of a moving impactor is used to determine the hardness.ISO 16859-1:2015 covers the determination of a dynamic hardness of metallic materials using seven different Leeb scales (HLD, HLS, HLE, HLDL, HLD+15, HLC, HLG).Metallic materials — Leeb hardness test — Part 1: Test method 1 Scope This part of ISO 16859 covers the determination of a dynamic hardness of metallic materials using seven different Leeb scales (HLD, HLS, HLE, HLDL, HLD+15, HLC, HLG). 2 Normative referencesISO 16859 consists of the following parts, under the general title Metallic materials — Leeb hardness test: — Part 1: Test method. — Part 2: Verification and calibration of the testing devices. — Part 3: Calibration of reference test blocks.
Para la mayoría de las aplicaciones de laboratorio, los autoclaves se ajustan a la temperatura de esterilización estándar de "121°C durante 20 minutos". Pero, ¿por qué estos números específicos? ¿Cómo consigue el autoclave una .The optimal temperature for sterilization typically ranges between 121°C (250°F) and 134°C (273°F), depending on the type of autoclave and the materials being sterilized.
leeb hardness test method|types of rockwell hardness test